上級
LibFuzzer (Cargo-Fuzz) インストゥルメンテーション付き Rust ターゲット¶


libFuzzer インストゥルメンテーション付き Rust ターゲットをテストする必要がありますか? このレッスンでは、 cargo-fuzz を使用した libFuzzer インストゥルメンテーション付き Rust ターゲットをテストする方法を順を追って説明します。
学習時間の目安: 15 分
このレッスンを終了すると、以下のことができるようになります。
- 不適切な入力検証の欠陥がある cargo-fuzz を使用した libFuzzer インストゥルメンテーション付き Rust ターゲットをコンパイルし、ファジングする。
- インデックス境界外の欠陥がある cargo-fuzz を使用した libFuzzer インストゥルメンテーション付き Rust ターゲットをコンパイルし、ファジングする。
レッスンを駆け足で
始める前に前提条件を確認します。
1.rust-cargo-fuzz.tgz をダウンロードし、rust-cargo-fuzz Docker イメージをビルドし、指定された Docker レジストリにプッシュします。
```{.sh .freemium }
docker build -t <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/rust-cargo-fuzz .
docker push <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/rust-cargo-fuzz
```
```{.sh .enterprise }
docker build -t $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/forallsecure/rust-cargo-fuzz .
docker push $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/forallsecure/rust-cargo-fuzz
```
-
Mayhem UI または Mayhem CLI で次の Mayhemfile を使用して
rust-cargo-fuzzDocker イメージに対して Mayhem ランを実行します。1 2 3 4 5 6 7
image: <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/rust-cargo-fuzz:latest duration: 90 project: rust target: rust-cargo-fuzz cmds: - cmd: /mayhemit/fuzz/target/x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu/release/mayhemit libfuzzer: true1 2 3 4 5 6 7
image: $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/forallsecure/rust-cargo-fuzz:latest duration: 90 project: rust target: rust-cargo-fuzz cmds: - cmd: /mayhemit/fuzz/target/x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu/release/mayhemit libfuzzer: true
以下が必要です。
- Docker がインストールされていること
- 有効なインターネット接続 (Docker Hub ベース イメージをプルするため)
ワン クリック テスト¶
下のボタンをクリックして libFuzzer インストゥルメンテーション付き Rust ターゲットのテストを開始します。最終確認ページに到達するまで [Next] をクリックし、[Start Run] をクリックします。
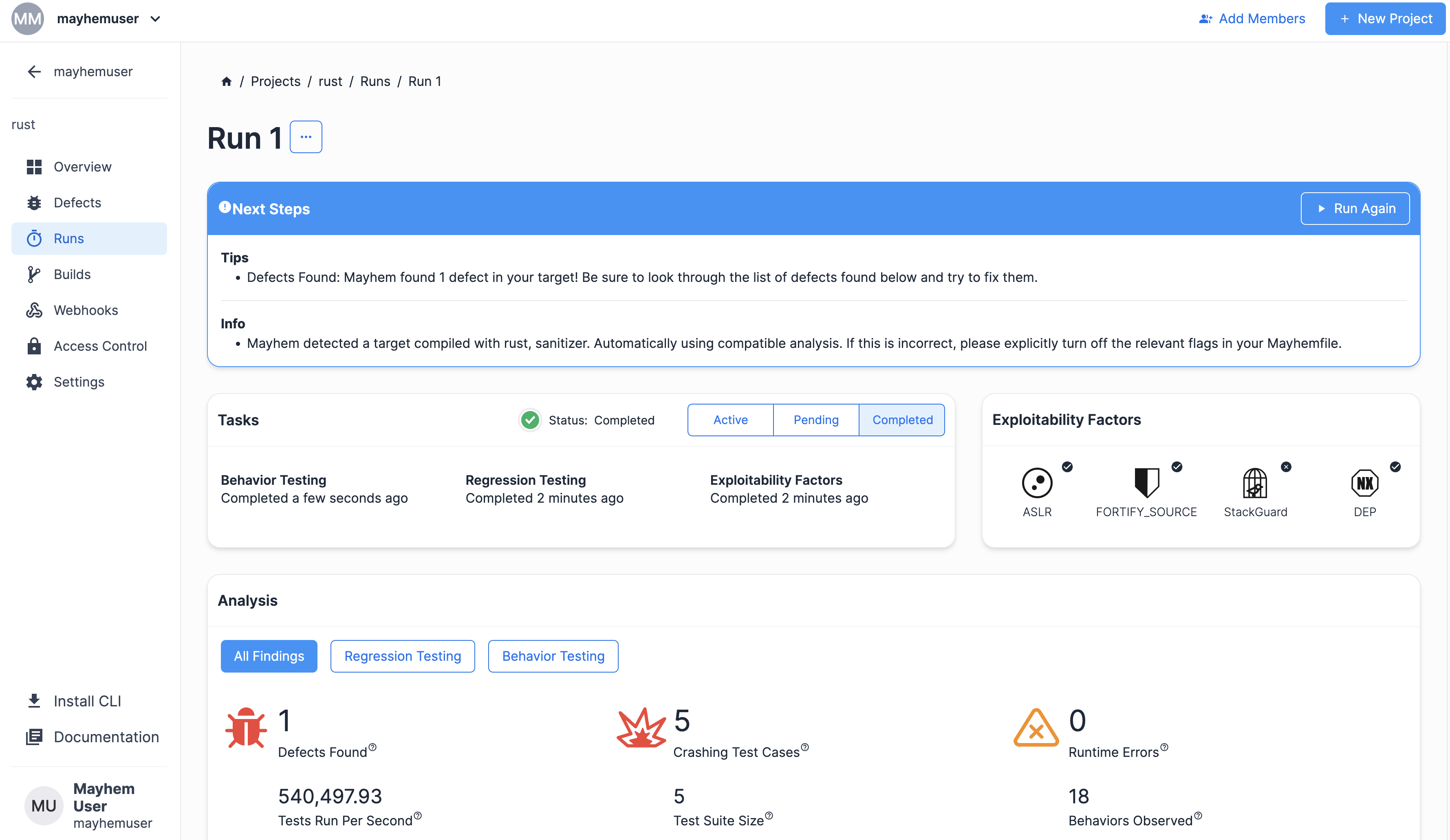
次のようなラン ページが表示されます。
Mayhem による libFuzzer インストゥルメンテーション付き Rust ターゲットのテストを確認したので、次に、Rust ターゲットをビルドする方法を順を追って説明します。
Cargo-Fuzz を使用した Rsut ターゲットのビルドとテスト¶
ファイル: rust-cargo-fuzz.tgz
上記の rust-cargo-fuzz.tgz をダウンロードして展開し、次のバグのある mayhemit.rs プログラムを見てみましょう。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | |
プログラムに外部クレート モジュール libfuzzer_sys がインポートされ、関数 fuzz_target! がファザーへのエントリポイントとして機能し、入力パラメーター data を受け取って、入力テスト ケース data に "bug" という単語が含まれているかどうかを確認しているのがわかります。入力が "bug" である場合、プログラムは不適切な入力検証の欠陥でクラッシュします。
次に rust-cargo-fuzz がどのようにビルドされるかを見てみましょう。関連する Dockerfile を見ると、以下の処理があるのがわかります。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | |
- 行 1: 必要な Rust および cargo-fuzz 依存関係を収集するため、
fuzzers/cargo-fuzz:0.10.0ベース イメージがインポートされています。 - 行 2: Docker コンテナーに
mayhemit.rsソース ファイルがコピーされています。 - 行 3-11: 新規 cargo パッケージ
mayhemitが作成され、cargo fuzz buildユーティリティがmayhemit実行ファイルをコンパイルするためにmayhemit.rsソース コードが適切なディレクトリにコピーされています。 - 行 14: ビルドされた Docker イメージのデフォルト実行ファイルとして
/mayhemit/fuzz/target/x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu/release/mayhemit実行ファイルが定義されています。
次に、docker build および docker push コマンドを使用して、Docker イメージをビルドして Docker Hub レジストリにプッシュする必要があります。
次に、docker build および docker push コマンドを使用して、実際に Docker イメージをビルドして Mayhem サーバーにプッシュする必要があります。$MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY は、プライベートな Mayhem Docker レジストリの URL を表します。
docker build -t <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/rust-cargo-fuzz .
docker push <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/rust-cargo-fuzz
docker build -t $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/forallsecure/rust-cargo-fuzz .
docker push $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/forallsecure/rust-cargo-fuzz
Info
mayhem login コマンドを使用して内部的な Mayhem Docker レジストリの URL を検索し、次のコマンドを使用して DOCKER_REGISTRY 環境変数を設定できます:
export DOCKER_REGISTRY=tutorial.forallsecure.com:5000
DOCKER_REGISTRY 環境変数に自身の Mayhem Docker レジストリ URL を設定する必要があります。
新しく作成した Docker イメージをパブリックな Docker Hub レジストリに正常にプッシュしたら、Mayhem UI から新規ランを作成し、<DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/rust-cargo-fuzz Docker イメージを検索します。Mayhemfile が次のようになっていることを確認します。
新しく作成した Docker イメージをプライベートな Mayhem Docker レジストリに正常にプッシュしたら、Mayhem UI から新規ランを作成し、forallsecure/rust-cargo-fuzz Docker イメージを検索します。Mayhemfile が次のようになっていることを確認します。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
新規ランの作成フローの最後に到達するまで [Next ] をクリックし、[Start Run] をクリックして Mayhem ランを実行します。次のようなラン ページが表示されます。
おめでとうございます! cargo-fuzz を使用した libFuzzer インストゥルメンテーション付き Rust ターゲットのテストが成功しました。
⚡ 現実的な演習: Cargo-Fuzz を使用した mayhemit-out-of-bounds Rust ターゲットのビルドとテスト¶
不適切な入力検証の欠陥がある Rust libFuzzer ターゲットのビルドおよびテスト方法がわかったところで、ソース コードを修正してインデックスの境界外の欠陥を検出できるかどうかやってみましょう。
ファイル: mayhemit-out-of-bounds-unsolved.zip
mayhemit.rsソース コードを変更し、配列境界外欠陥を追加します。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | |
docker buildコマンドを使用してDockerfileを再ビルドし、結果の Docker イメージを<DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-boundsとしてタグ付けします。docker tagおよびdocker pushコマンドを使用してパブリックな Docker Hub レジストリに<DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-boundsDocker イメージをプッシュします。- Mayhem UI または Mayhem CLI を使用して
<DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-boundsDocker イメージをファジングします。Mayhemfileが適切に設定されていることを確認します。
docker buildコマンドを使用してDockerfileを再ビルドし、結果の Docker イメージを$MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-boundsとしてタグ付けします。docker tagおよびdocker pushコマンドを使用してプライベートな Mayhem Docker レジストリに$MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-boundsDocker イメージをプッシュします。- Mayhem UI または Mayhem CLI を使用して
$MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-boundsDocker イメージをテストします。Mayhemfileが適切に設定されていることを確認します。
🔍 確認Cargo-Fuzz を使用した mayhemit-out-of-bounds Rust ターゲットのビルドとテスト¶
解答
模範解答: mayhemit-out-of-bounds-solved.tgz
まず、fuzz_target! 関数を使用してファズ入力を解析したとき、入力テスト ケース "bug" がインデックス境界外エラーを発生させるよう、インデックス境界外のコード スニペットを追加します。これは、data.len() >= 3 かつ data.len() < 5 のときだけコードが if 文に進むからです。そのため、変数 x に data[10] を設定しようとすると、インデックス境界外エラーが発生します。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | |
次に、Dockerfile と同じディレクトリで docker build コマンドを実行し、結果の Docker イメージに <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-bounds というタグを付けます。
次に、Dockerfile と同じディレクトリで docker build コマンドを実行し、結果の Docker イメージに $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-bounds というタグを付けます。
docker build -f Dockerfile -t <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-bounds .
docker build -f Dockerfile -t $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-bounds .
次に、<DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-bounds Docker イメージにタグを付けてパブリックな Docker Hub レジストリにプッシュします。
次に、$MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-bounds Docker イメージにタグを付けてプライベートな Mayhem Docker レジストリにプッシュします。
docker push <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-bounds
docker push $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-bounds
make build
make push
最後に、Mayhem UIMayhem UI または Mayhem CLI を使用して、アップロードされた <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-bounds Docker イメージに対して Mayhem ランを実行します。Mayhemfile は次のようになっているはずです。
最後に、Mayhem UIMayhem UI または Mayhem CLI を使用して、アップロードされた $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-bounds Docker イメージに対して Mayhem ランを実行します。Mayhemfile は次のようになっているはずです。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
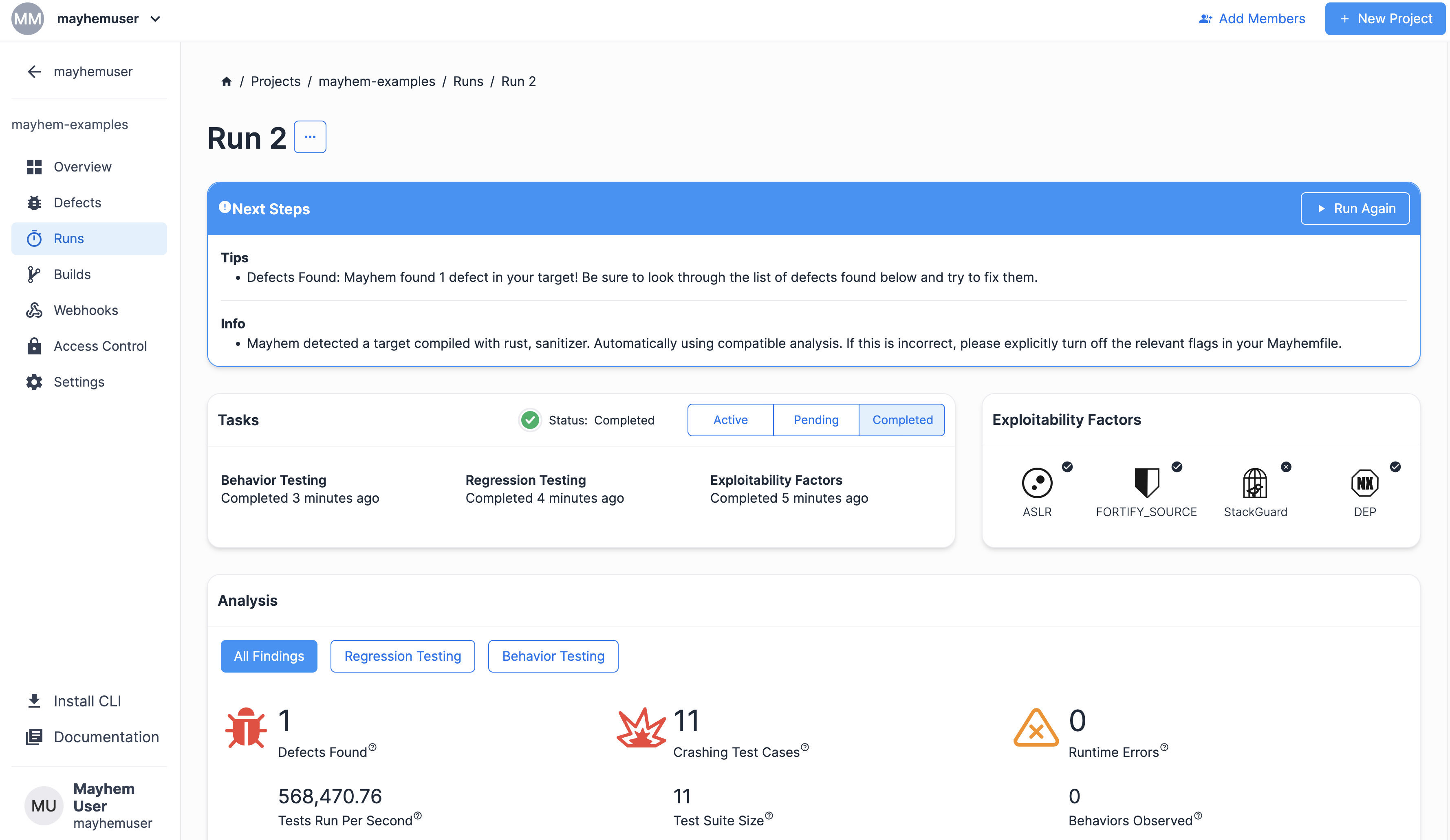
最終的なラン ページは次のように表示されるはずです。
おめでとうございます! Mayhem がインデックス境界外の欠陥を発見しました。スクラッチから libFuzzer インストゥルメンテーション付き Rust ターゲットをビルドし、cargo-fuzz を使用してバグを検出できました。
✏️ まとめと振り返り¶
このレッスンでは、cargo-fuzz を使用した libFuzzer インストゥルメンテーション付き Rust ターゲットを Mayhem でファジングする方法を学びました。
学習内容
1. cargo-fuzz を使用して不適切な入力検証の欠陥がある libFuzzer インストゥルメンテーション付き Rust ターゲットをビルドし、テストする。
-
ソース コードには次の欠陥が含まれているはずです:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
fuzz_target!(|data: &[u8]| { if data.len() >= 3 { if data[0] == 'b' as u8 { if data[1] == 'u' as u8 { if data[2] == 'g' as u8 { process::abort(); } } } } }); -
cargo-fuzz を使用して Rust ターゲットをファジングするには、次の
DockerfileおよびMayhemfileを使用して Rust プログラムを含む Docker イメージをビルドし、Mayhem でファジングを実行します。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
FROM fuzzers/cargo-fuzz:0.10.0 COPY mayhemit.rs . RUN export USER=root && \ cargo new mayhemit && \ cd mayhemit && \ cargo fuzz init && \ cd fuzz && \ sed -i 's/fuzz_target_1/mayhemit/g' Cargo.toml && \ rm fuzz_targets/fuzz_target_1.rs && \ cp /mayhemit.rs /mayhemit/fuzz/fuzz_targets && \ cargo fuzz build # Set to fuzz! ENTRYPOINT [] CMD ["/mayhemit/fuzz/target/x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu/release/mayhemit"]1 2 3 4 5 6 7
image: <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/rust-cargo-fuzz:latest duration: 90 project: rust target: rust-cargo-fuzz cmds: - cmd: /mayhemit/fuzz/target/x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu/release/mayhemit libfuzzer: true1 2 3 4 5 6 7
image: $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/forallsecure/rust-cargo-fuzz:latest duration: 90 project: rust target: rust-cargo-fuzz cmds: - cmd: /mayhemit/fuzz/target/x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu/release/mayhemit libfuzzer: true
2.cargo-fuzz を使用してインデックス境界外の欠陥がある libFuzzer インストゥルメンテーション付き Rust ターゲットをビルドし、テストする。
-
ソース コードには次の欠陥が含まれているはずです:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
fuzz_target!(|data: &[u8]| { if data.len() >= 3 && data.len() < 5 { if data[0] == 'b' as u8 { if data[1] == 'u' as u8 { if data[2] == 'g' as u8 { let x; x = data[10]; } } } } }); -
cargo-fuzz を使用して Rust ターゲットをファジングするには、次の
DockerfileおよびMayhemfileを使用して Rust プログラムを含む Docker イメージをビルドし、Mayhem でファジングを実行します。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
FROM fuzzers/cargo-fuzz:0.10.0 COPY mayhemit.rs . RUN export USER=root && \ cargo new mayhemit && \ cd mayhemit && \ cargo fuzz init && \ cd fuzz && \ sed -i 's/fuzz_target_1/mayhemit/g' Cargo.toml && \ rm fuzz_targets/fuzz_target_1.rs && \ cp /mayhemit.rs /mayhemit/fuzz/fuzz_targets && \ cargo fuzz build # Set to fuzz! ENTRYPOINT [] CMD ["/mayhemit/fuzz/target/x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu/release/mayhemit"]1 2 3 4 5 6 7
image: <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-bounds:latest duration: 90 project: mayhem-examples target: rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-bounds cmds: - cmd: /mayhemit/fuzz/target/x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu/release/mayhemit libfuzzer: true1 2 3 4 5 6 7
image: $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-bounds:latest duration: 90 project: mayhem-examples target: rust-cargo-fuzz-mayhemit-out-of-bounds cmds: - cmd: /mayhemit/fuzz/target/x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu/release/mayhemit libfuzzer: true