上級
Atheris を使用した LibFuzzer インストゥルメンテーション付き Python ターゲット¶


テスト対象は Python ターゲットですか? このレッスンでは、Atheris モジュールを使用した LibFuzzer インストゥルメンテーション付き Python ターゲットをテストする方法を順を追って説明します。
学習時間の目安: 15 分
このレッスンを終了すると、以下のことができるようになります。
- キャッチされない例外の欠陥がある Atheris モジュールを使用した libFuzzer インストゥルメンテーション付き Python ターゲットをコンパイルし、ファジングする。
- インデックス境界外の欠陥がある Atheris モジュールを使用した libFuzzer インストゥルメンテーション付き Python ターゲットをコンパイルし、ファジングする。
レッスンを駆け足で
始める前に前提条件を確認します。
-
python-atheris.tgz をダウンロードし、
python-atherisDocker イメージをビルドし、指定された Docker レジストリにプッシュします。docker build -f Dockerfile -t <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris . docker push <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atherisdocker build -f Dockerfile -t $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/forallsecure/python-atheris . docker push $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/forallsecure/python-atheris -
Mayhem UI または Mayhem CLI で次の Mayhemfile を使用して
forallsecure/python-atherisDocker イメージに対して Mayhem ランを実行します。1 2 3 4 5 6 7
image: <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris:latest duration: 90 project: mayhem-examples target: python-atheris cmds: - cmd: /mayhemit.py libfuzzer: true1 2 3 4 5 6 7
image: $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/forallsecure/python-atheris:latest duration: 90 project: python target: python-atheris cmds: - cmd: /mayhemit.py libfuzzer: true
以下が必要です。
- Docker がインストールされていること
- 有効なインターネット接続 (Docker Hub ベース イメージをプルするため)
ワン クリック テスト¶
下のボタンをクリックして Python ターゲットのテストを開始します。最終確認ページに到達するまで [Next] をクリックし、[Start Run] をクリックします。
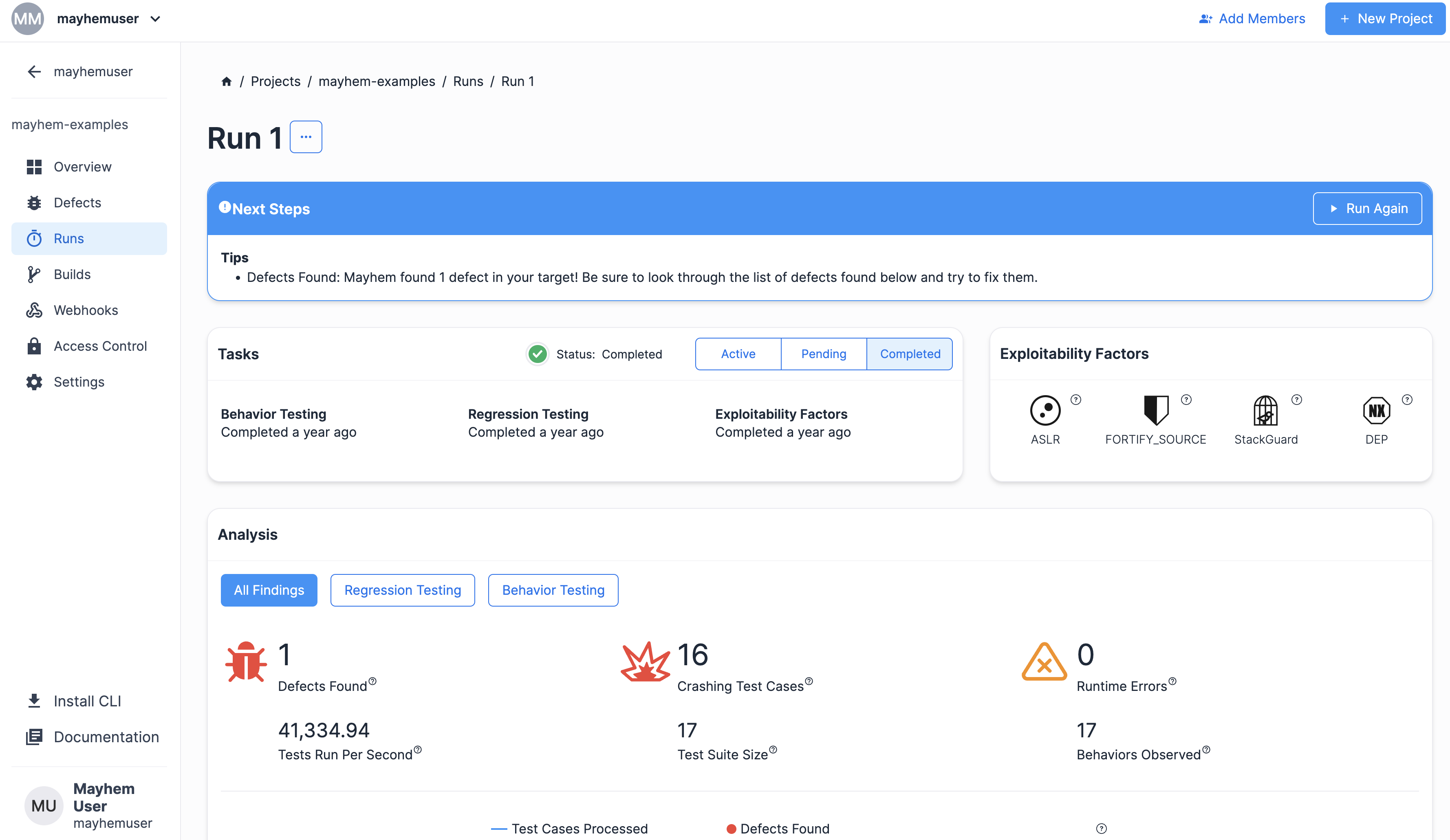
次のようなラン ページが表示されます。
Mayhem による Python ターゲットのテストを確認したので、次に、どのように Python ターゲットがビルドされたのかを順を追って説明します。
Mayhem での Atheris を使用した Python ターゲットのテスト¶
ファイル: python-atheris.tgz
上記の python-atheris.tgz をダウンロードして展開し、次の脆弱性のある mayhemit.py プログラムを見てみましょう。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | |
Info
Python でインデックスを使用して bytestring にアクセスすると、整数が返されます。そのため、string 文字のユニコード コード ポイントを表現する整数を返す ord() が使用されています。data[0] == ord('b') が true に評価される等の条件を使用しているのはそのためです。
Warning
atheris ハーネス スクリプトに複数のターゲット (たとえば foo および bar) が含まれており、コマンド ライン引数 (例: foo) によってどれを選択するかを制御している場合、atheris.Setup の呼び出しを実行する前に、(sys.argv.pop(1) などを使用して) sys.argv から該当引数を除外する必要があります。そうでなければ、atheris は余分な (未知の) 引数をテスト ターゲットに渡します。余分な引数が削除されない場合、 Mayhem ランは余分な引数による "unexpected libFuzzer argument" エラーで失敗します。
atheris および sys モジュールがプログラムにインポートされ、関数 TestOneInput が入力パラメーター data を受け取ることがわかります。この入力パラメーターをチェックして "bug" というつづりかどうかをチェックしています。"bug" である場合、行 12でキャッチされない例外の欠陥によってプログラムがクラッシュします。
行 12 および 13で、atheris モジュールは Setup および Fuzz 関数を使用してテスト エントリポイントをセットアップしています。
次に、関連する Dockerfile を見て、python-atheris がどのようにビルドされるかを確認しましょう。
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
- 行 1: ビルド ステージ Docker コンテナー内に必要な
atheris依存関係を用意するため、ベース環境としてfuzzers/atheris:2.0.7-python3.9ベース イメージが設定されています。 - 行 2:
fuzzers/atheris:2.0.7-python3.9Docker コンテナーにmayhemit.pyソース ファイルがコピーされています。 - 行 3: ビルドされた Docker イメージのデフォルト実行ファイルとして
/mayhemit.py実行ファイルが設定されています。
Note
python-atheris ターゲットに必要なコンパイル ステップがないことに気づくかもしれません。コンパイルが必要な他の言語のターゲットと異なり、Python はインタープリター言語であるため、コンパイルは必要ありません。
次に、docker build および docker push コマンドを使用して、Docker イメージをビルドして Docker Hub レジストリにプッシュする必要があります。python-atheris フォルダー内にいることを確認し、次のコマンドを実行します。
次に、docker build および docker push コマンドを使用して、Docker イメージをビルドして Mayhem サーバーにプッシュする必要があります。$MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY は、プライベートな Mayhem Docker レジストリの URL を表す環境変数です。python-atheris フォルダー内にいることを確認し、次のコマンドを実行します。
docker build -f Dockerfile -t <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris .
docker push <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris
docker build -f Dockerfile -t $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/forallsecure/python-atheris .
docker push $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/forallsecure/python-atheris
Info
mayhem login コマンドを使用して内部的な Mayhem Docker レジストリの URL を検索し、次のコマンドを使用して DOCKER_REGISTRY 環境変数を設定できます:
export DOCKER_REGISTRY=tutorial.forallsecure.com:5000
DOCKER_REGISTRY 環境変数に自身の Mayhem Docker レジストリ URL を設定する必要があります。
新しく作成した Docker イメージを Docker Hub レジストリに正常にプッシュしたら、Mayhem UI から新規ランを作成し、<DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris Docker イメージを検索します。Mayhemfile が次のようになっていることを確認します。
新しく作成した Docker イメージをプライベートな Mayhem Docker レジストリに正常にプッシュしたら、Mayhem UI から新規ランを作成し、forallsecure/python-atheris Docker イメージを検索します。Mayhemfile が次のようになっていることを確認します。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
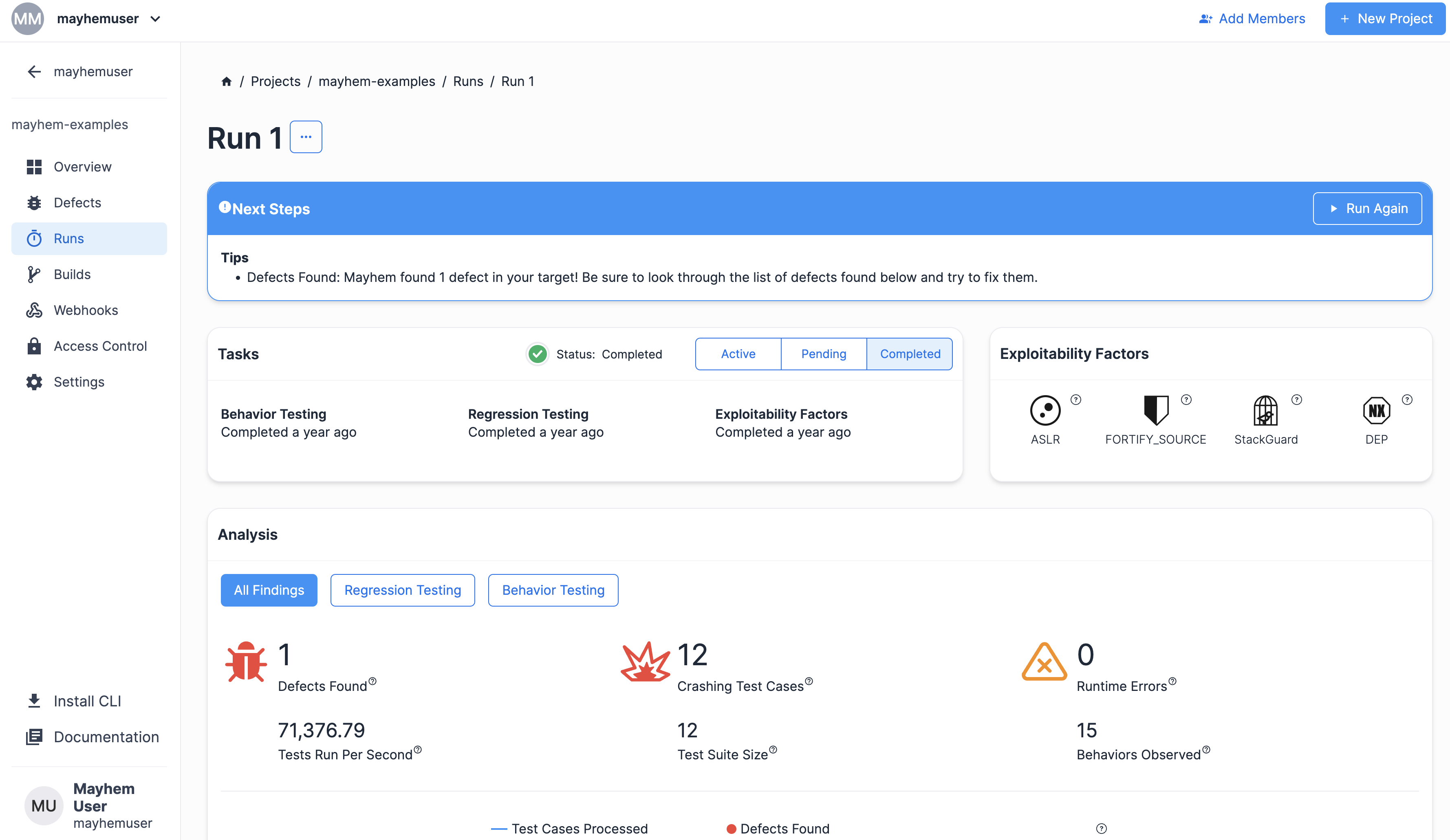
新規ラン作成フローの最終確認ページに到達するまで [Next] をクリックし、[Start Run] をクリックして Mayhem ランを実行します。次のようなラン ページが表示されます。
おめでとうございます! atheris ファザー モジュールを使用した Python ターゲットのテストが成功しました。
⚡ 現実的な演習: Atheris を使用した mayhemit-out-of-bounds Python ターゲットのビルドとテスト¶
キャッチされない例外の欠陥がある Python ターゲットのビルドおよびテスト方法がわかったところで、ソース コードを修正してインデックス境界外の欠陥を検出できるかどうかやってみましょう。
ファイル: mayhemit-out-of-bounds-unsolved.zip
手順
mayhemit.pyソース コードを変更し、次の行を追加して配列境界外欠陥を設定します。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
docker buildコマンドを使用してDockerfileを再ビルドし、結果の Docker イメージを<DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-boundsとしてタグ付けします。docker pushコマンドを使用してパブリックな Docker Hub レジストリに<DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-boundsDocker イメージをプッシュします。- Mayhem UI または Mayhem CLI を使用して
<DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-boundsDocker イメージをファジングします。Mayhemfileが適切に設定されていることを確認します。
docker buildコマンドを使用してDockerfileを再ビルドし、結果の Docker イメージを$MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-boundsとしてタグ付けします。docker pushコマンドを使用してプライベートな Mayhem Docker レジストリに$MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-boundsDocker イメージをプッシュします。- Mayhem UI または Mayhem CLI を使用して
$MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-boundsDocker イメージをテストします。Mayhemfileが適切に設定されていることを確認します。
🔍 確認Atheris を使用した mayhemit-out-of-bounds Python ターゲットのビルドとテスト¶
解答
模範解答: mayhemit-out-of-bounds-solved.zip
まず、TestOneInput 関数をファジングしたとき、入力テスト ケース "bug" がインデックス境界外エラーを発生させるよう、最大長の制約 len(data) < 5 および誤った呼び出し data[10] を追加します。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | |
次に、Dockerfile と同じディレクトリで docker build コマンドを実行し、結果の Docker イメージに <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds というタグを付けます。
次に、Dockerfile と同じディレクトリで docker build コマンドを実行し、結果の Docker イメージに $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds というタグを付けます。
docker build -f Dockerfile -t <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds .
docker build -f Dockerfile -t $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds .
次に、<DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds Docker イメージにタグを付けてパブリックな Docker Hub レジストリにプッシュします。
次に、$MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds Docker イメージにタグを付けてプライベートな Mayhem Docker レジストリにプッシュします。
docker push <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds
docker push $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds
別の方法として、付属の Makefil を使用し、MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY` 環境変数を設定して次のコマンドを実行することで、簡単に結果の Docker イメージをビルドし、プッシュすることもできます。
make build
make push
最後に、Mayhem UI または Mayhem CLI を使用して、アップロードされた <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds Docker イメージに対して Mayhem ランを実行します。Mayhemfile は次のようになっているはずです。
最後に、Mayhem UI または Mayhem CLI を使用して、アップロードされた $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds Docker イメージに対して Mayhem ランを実行します。Mayhemfile は次のようになっているはずです。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
最終的なラン ページは次のように表示されるはずです。
おめでとうございます! Mayhem がインデックス境界外の欠陥を発見しました。スクラッチから Python ターゲットをビルドし、Atheris ファザー モジュールを使用してバグを検出できました。
✏️ まとめと振り返り¶
このレッスンでは、Atheris ファザー モジュールおよび Mayhem を使用して libFuzzer インストゥルメンテーション付き Python ターゲットをファジングする方法を学びました。
学習内容
1. Atheris を使用した LibFuzzer インストゥルメンテーション付き Python ターゲットをビルドおよびテストしてキャッチされない例外の欠陥を検出する。
-
ソース コードには次の欠陥が含まれているはずです:
1 2 3 4 5 6
def TestOneInput(data): if len(data) >= 3: if data[0] == ord('b'): if data[1] == ord('u'): if data[2] == ord('g'): raise Exception("Made it to the bug!") -
Atheris を使用して Python ターゲットをファジングするには、次の Dockerfile を使用して Python プログラムを含む Docker イメージをビルドします。
1 2 3 4 5 6
FROM fuzzers/atheris:2.0.7-python3.9 COPY mayhemit.py /mayhemit.py # Set to fuzz! ENTRYPOINT [] CMD ["/mayhemit.py"]
2. Atheris を使用した LibFuzzer インストゥルメンテーション付き Python ターゲットをビルドおよびファジングしてインデックス境界外の欠陥を検出する。
-
ソース コードには次の欠陥が含まれているはずです:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
def TestOneInput(data): if len(data) >= 3 and len(data) < 5: if data[0] == ord('b'): if data[1] == ord('u'): if data[2] == ord('g'): print("Made it to the bug!") return data[10] -
Atheris を使用して Python ターゲットをファジングするには、次の Dockerfile を使用して Python プログラムを含む Docker イメージをビルドします。
1 2 3 4 5 6
FROM fuzzers/atheris:2.0.7-python3.9 COPY mayhemit.py /mayhemit.py # Set to fuzz! ENTRYPOINT [] CMD /mayhemit.py