advanced
Python Targets with LibFuzzer Instrumentation via Atheris¶


Need to test a Python target? We'll walk you through how to test Python targets using libFuzzer instrumentation via the Atheris module!
Estimated Time: 15 minutes
By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
- Build and fuzz a Python target with libFuzzer instrumentation using the Atheris module for an uncaught exception defect.
- Build and fuzz a Python target with libFuzzer instrumentation using the Atheris modile for an index out-of-bounds defect.
Run through the lesson:
See prerequisites before beginning.
-
Download the python-atheris.tgz and build the
python-atherisDocker image, and push it to the specified Docker Registry:docker build -f Dockerfile -t <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris . docker push <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atherisdocker build -f Dockerfile -t $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/forallsecure/python-atheris . docker push $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/forallsecure/python-atheris -
Execute a Mayhem run on the
forallsecure/python-atherisDocker image using either the Mayhem UI or Mayhem CLI with the following Mayhemfile:1 2 3 4 5 6 7
image: <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris:latest duration: 90 project: mayhem-examples target: python-atheris cmds: - cmd: /mayhemit.py libfuzzer: true1 2 3 4 5 6 7
image: $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/forallsecure/python-atheris:latest duration: 90 project: python target: python-atheris cmds: - cmd: /mayhemit.py libfuzzer: true
You will need the following:
- Docker installed.
- A valid Internet connection (for pulling Docker Hub base images)
One Click Testing¶
Click on the button below to start testing a Python target! Click Next until you reach the final confirmation page and then hit Start Run!
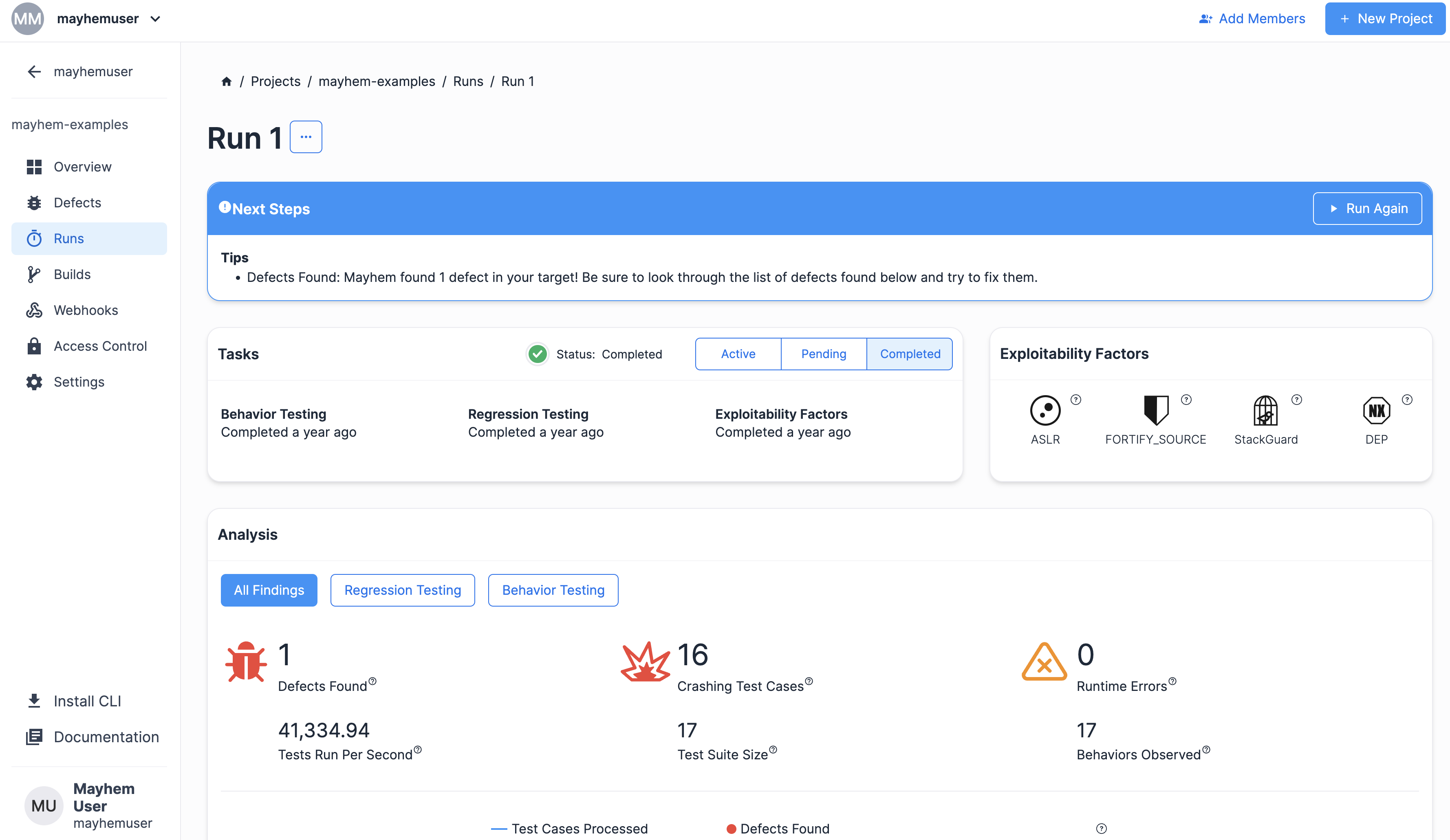
You should see a Run page similar to the following:
Now that you've seen Mayhem testing a Python target, let's walk through end-to-end how the Python target was built!
Testing a Python Target with Atheris¶
File: python-atheris.tgz
Download and extract the above python-atheris.tgz and take a look at the following vulnerable mayhemit.py program:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | |
Info
Indexing on a bytestring in Python will return an integer. Therefore, the ord() function is used to return an integer representing the unicode code point of a string character. This is why setting the condition of data[0] == ord('b') evaluates to true and so on.
Warning
If your atheris harness script contains multiple targets (say foo and bar) and selecting between them is controlled through a command line argument (e.g., foo) you will have to omit that argument from sys.argv (e.g., through sys.argv.pop(1)) before you perform your atheris.Setup invocation or atheris will pass the extra (unknown) argument to your underlying testing target. If the extra argument isn't removed, your Mayhem run will fail with an "unexpected libFuzzer argument" error for the extra argument.
Here we see that the atheris and sys modules been imported in the program and that a function TestOneInput takes in the input parameter data, which checks to see if the word "bug" is spelled. If so, the program crashes with an uncaught exception defect on line 12.
Then on lines 12 and 13, the atheris module sets up the testing entrypoint by using its Setup and Fuzz functions, respectively.
Let's now take a look at the associated Dockerfile to see how the python-atheris target will be built:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
- Line 1: The
fuzzers/atheris:2.0.7-python3.9base image is set as the base environment to provide the necessaryatherisdependencies within a build stage Docker container. - Line 2: The
mayhemit.pysource file is copied into thefuzzers/atheris:2.0.7-python3.9Docker container. - Line 3: The
/mayhemit.pyexecutable is set as the default executable for the resulting Docker image.
Note
You may have noticed that there is no compilation step required for the python-atheris target. Unlike other language targets that need to be compiled, Python is an interpreted language so no compilation is required here!
Next, we need to build and push the resulting Docker image to the Docker Hub registry using the docker build and docker push commands. Make sure you're within the python-atheris folder and execute the following commands:
Next, we need to build and push the resulting Docker image to the Mayhem server using the docker build and docker push commands, where $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY is an environment variable representing the URL of the private Mayhem Docker Registry. Make sure you're within the python-atheris folder and execute the following commands:
docker build -f Dockerfile -t <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris .
docker push <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris
docker build -f Dockerfile -t $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/forallsecure/python-atheris .
docker push $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/forallsecure/python-atheris
Info
You can use the mayhem login command to find your internal Mayhem Docker Registry URL and run the following command to set the DOCKER_REGISTRY environment variable, like so:
export DOCKER_REGISTRY=tutorial.forallsecure.com:5000
Here, we've provided an example Mayhem Docker registry URL, but you will need to set the DOCKER_REGISTRY environment variable for your specific Mayhem Docker Registry URL.
Upon successfully pushing the newly created Docker image to the Docker Hub registry, create a new run via the Mayhem UI and search for the <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris Docker image. Confirm that your Mayhemfile looks similar to the following:
Upon successfully pushing the newly created Docker image to the private Mayhem Docker Registry, create a new run via the Mayhem UI and search for the forallsecure/python-atheris Docker image. Confirm that your Mayhemfile looks similar to the following:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
Now just click Next until you reach the final confirmation page of the create new run flow and hit Start Run to execute your Mayhem run! You should see a Run page similar to the following:
Congratulations! You just tested a Python target with the atheris fuzzer module!
⚡ Real World Exercise: Building and Testing the mayhemit-out-of-bounds Python Target with Atheris¶
Now that you know how to build and test a Python target with an uncaught exception defect, let's see if you can modify the source code to use an index out-of-bounds defect instead.
Files: mayhemit-out-of-bounds-unsolved.zip
Instructions:
-
Modify the
mayhemit.pysource code and add the following lines to initialize the array out-of-bounds defect:1 2 3 4 5 6 7
def TestOneInput(data): if len(data) >= 3 and len(data) < 5: if data[0] == ord('b'): if data[1] == ord('u'): if data[2] == ord('g'): print("Made it to the bug!") return data[10] -
Rebuild the
Dockerfileusing thedocker buildcommand and tag the resulting Docker image as<DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds. - Push the
<DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-boundsDocker image to the public Docker Hub registry using thedocker pushcommand. - Fuzz the
<DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-boundsDocker image using either the Mayhem UI or Mayhem CLI. Make sure to set the associatedMayhemfileaccordingly.
- Rebuild the
Dockerfileusing thedocker buildcommand and tag the resulting Docker image as$MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds. - Push the
$MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-boundsDocker image to the private Mayhem Docker registry using thedocker pushcommand. - Test the
$MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-boundsDocker image using either the Mayhem UI or Mayhem CLI. Make sure to set the associatedMayhemfileaccordingly.
🔍 Review It! Building and Testing the mayhemit-out-of-bounds Python Target with Atheris¶
Solution
Solution: mayhemit-out-of-bounds-solved.zip
First things first, you needed to add the max length constraint len(data) < 5 and the erroneous call for data[10] to the TestOneInput function so that when the TestOneInput function is fuzzed, the input test case "bug" will trigger the corresponding index out-of-bounds error.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | |
Then, you needed to run the docker build command in the same directory as the Dockerfile and proceed to tag the resulting Docker image as <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds:
Then, you needed to run the docker build command in the same directory as the Dockerfile and proceed to tag the resulting Docker image as $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds:
docker build -f Dockerfile -t <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds .
docker build -f Dockerfile -t $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds .
Next, you had to push the <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds Docker image to the public Docker Hub registry:
Next, you had to push the $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds Docker image to the private Mayhem Docker registry:
docker push <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds
docker push $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds
Alternatively, you could have also used the included Makefile to easily build and push the resulting Docker image by setting a MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY environment variable and running the following commands:
make build
make push
Lastly, you could have executed a Mayhem run on the uploaded <DOCKERHUB_USERNAME>/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds Docker image using either the Mayhem UI or Mayhem CLI. As long as your Mayhemfile looked similar to the following:
Lastly, you could have executed a Mayhem run on the uploaded $MAYHEM_DOCKER_REGISTRY/python-atheris-mayhemit-out-of-bounds Docker image using either the Mayhem UI or Mayhem CLI. As long as your Mayhemfile looked similar to the following:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
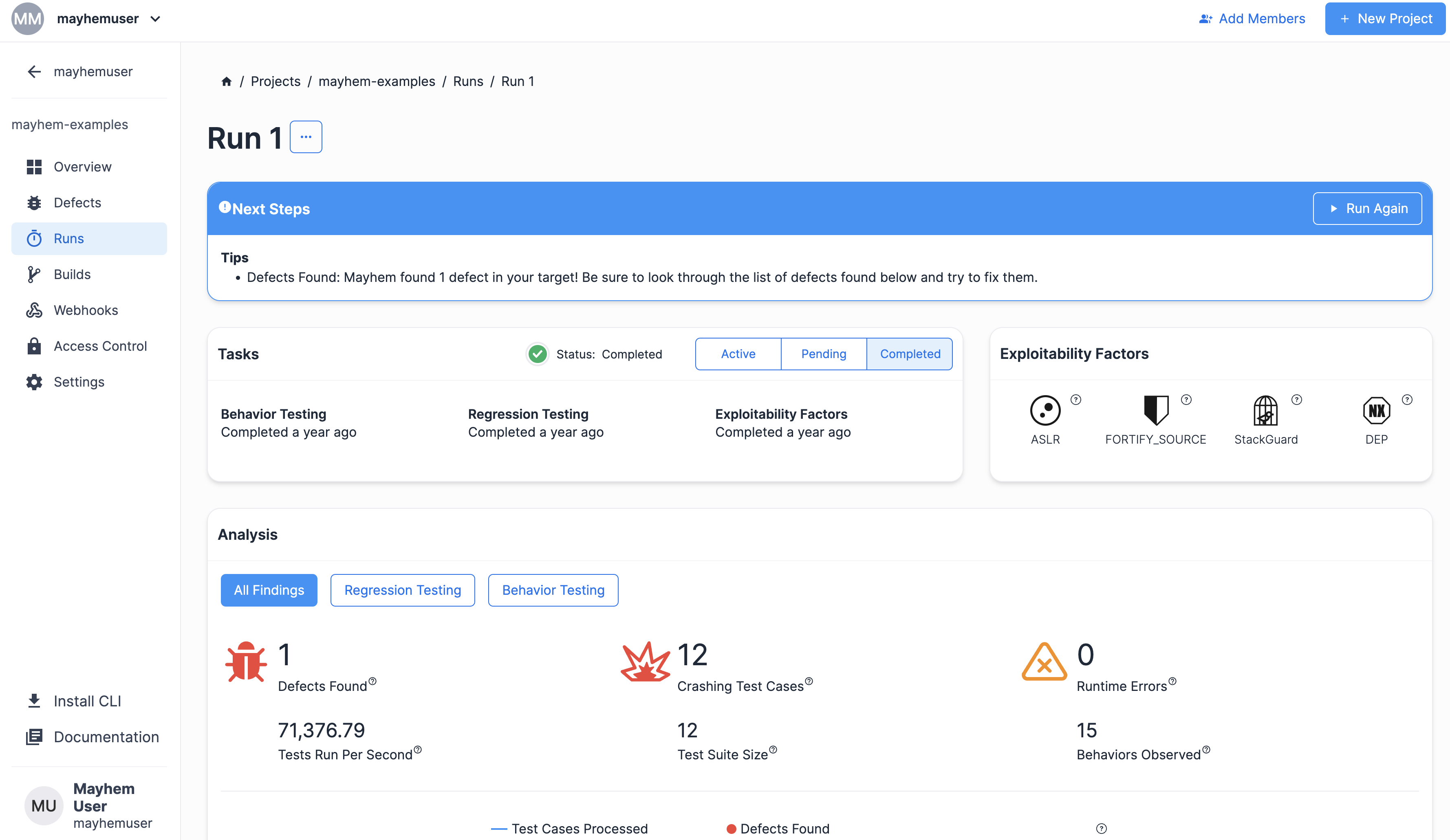
Your final Run page should have looked like the following:
Congratulations! Mayhem found the array out-of-bounds defect that you added! You just built a Python target from scratch and used the Atheris fuzzer module to detect the vulnerability that you added!
✏️ Summary and Recap¶
In this lesson, you learned how to fuzz Python targets with libFuzzer instrumentation using the Atheris fuzzer module and Mayhem!
I learned how to...
1. Build and test a Python target with libFuzzer instrumentation using the Atheris module for an uncaught exception defect.
-
The source code should contain the following defect:
1 2 3 4 5 6
def TestOneInput(data): if len(data) >= 3: if data[0] == ord('b'): if data[1] == ord('u'): if data[2] == ord('g'): raise Exception("Made it to the bug!") -
Then, to fuzz the Python target with Atheris, use the following Dockerfile to build the Docker image containing the Python program:
1 2 3 4 5 6
FROM fuzzers/atheris:2.0.7-python3.9 COPY mayhemit.py /mayhemit.py # Set to fuzz! ENTRYPOINT [] CMD ["/mayhemit.py"]
2. Build and fuzz a Python target with libFuzzer instrumentation using the Atheris module for an index out-of-bounds defect.
-
The source code should contain the following defect:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
def TestOneInput(data): if len(data) >= 3 and len(data) < 5: if data[0] == ord('b'): if data[1] == ord('u'): if data[2] == ord('g'): print("Made it to the bug!") return data[10] -
Then, to fuzz the Python target with Atheris, use the following Dockerfile to build the Docker image containing the Python program:
1 2 3 4 5 6
FROM fuzzers/atheris:2.0.7-python3.9 COPY mayhemit.py /mayhemit.py # Set to fuzz! ENTRYPOINT [] CMD /mayhemit.py